Controlling the amount of air in a conventional pressure tank is key in providing an efficient and reliable pumped water system. Last month, we described the compressor-based air-charging systems that use water-level probes to control the air charge in larger conventional tanks. In smaller residential systems, simpler, less expensive air-charging devices are common. The type of charging system used depends on whether the water system uses a suction-type pump, like a shallow well jet pump, or a pressure pump, like a submersible or deep well jet pump.
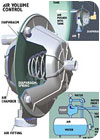
Jet Pump Systems
Figure 1 shows a jet pump system. An air volume control (AVC) is mounted on the side of the tank and plumbed to the suction side of the jet pump with a small tube. When the pump turns on, the reduced pressure created in the AVC draws in a small charge of air, which then is released into the tank when the pump shuts off. The design of the valve enables it to control the water level by drawing air from the tank or outside atmosphere, depending on the level of water in the tank. These valves are very effective, but must be kept clean to function properly.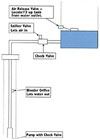
Submersible Pump Systems
Figure 2 is a schematic of a submersible pump system. It consists of a bleeder orifice, a snifter valve, and an air release valve. The bleeder orifice, installed in the drop pipe around 10 feet or so below the wellhead, acts as a drain port. At the end of each pumping cycle, the water in the pipe between the tank and the orifice drains out through the bleeder back onto the well. It is designed to seal when the pump is running and to open up when the pump shuts off.The snifter valve, typically mounted on a tapped check valve between the wellhead and the tank, allows air into the drop pipe so that the water can be released through the bleeder orifice when the pump shuts off. A snifter valve looks like a valve stem on a tire, but it has a very weak spring or no spring at all to function properly in this application.
At the beginning of the next pumping cycle, the air in the drop pipe between the bleeder orifice and the snifter valve is pushed into the pressure tank ahead of the water. More air is added each pump cycle than is needed to replenish the air absorbed into the water, so an air release valve is needed to purge the excess air from the tank.
The air release valves come in several configurations and are mounted on the side of the tank in the fitting provided by the tank manufacturer. An air release valve simply is a float valve, similar to a toilet bowl float valve, which opens when the water level is below the float to let air escape and closes when the water level raises and pushes up on the float.
One of the common failure modes in this type of air-charge system is clogged components. Iron algae, calcium or other minerals can foul the tiny openings in snifter valves, rendering them inoperable. The problem can be remedied easily by cleaning or replacing the core. Make sure the replacement core is designed for this application, that is, with a weak spring or no spring. A standard automobile or bicycle core will not work.
As with snifter valves, contamination is an air release valve's worst enemy. Minerals or iron bacteria can clog the air orifice or jam the float, rendering the air release system inoperable, leading to a water-logged tank, or one with excessive air, which will inconvenience your customer and may damage the pump and/or controls.
With the added maintenance, extra cost and possible reduced drawdown of conventional tanks vs. captive-air tanks, why would someone choose the former over the latter? One good reason is the beneficial side of their biggest drawback the fact that they absorb air into the water. Air is an excellent oxidizer of iron, hydrogen sulfide and other dissolved contaminants, so the use of a conventional tank may eliminate the need for a separate oxidation contact tank or chemical treatment to fix contaminated water.
The choice of pressure tank and other system components is important to the long-term operation of the water system and to the satisfaction of your customer. As I have said in the past, use the best components you can find and install them in accordance with local and national codes and practices. Nothing is more important to the success of your business than a bunch of happy customers.
Next month, we will look into the whys and hows of check valves. 'Til then.... ND



Report Abusive Comment