Most readers will have enough understanding of the word “ion” to associate it with chemistry class. Just the word itself can immediately evoke fear in those who dreaded the subject in their school days. The purpose of this article is to simplify the understanding of this amazing process and to familiarize readers with the capabilities and uses of ion exchange.
Ions simply are charged particles. Most often when we talk about ions, we think of charged particles that are free-floating, or dissolved, in a solution. And most of the time we think of water as the solvent for such solutions.
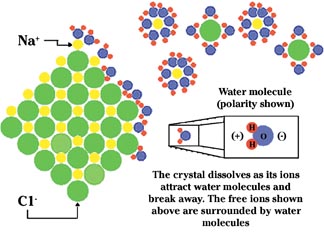
Ions come from natural or manmade salts or minerals that dissolve in water. Since it is easy to visualize granules of table salt dissolving in water, let's use it for discussion.
As its chemical name implies, table salt is composed of two companion ions - sodium and chloride. When they dissolve, the atoms that make up granules of table salt literally are surrounded by water molecules and carried off into solution (see Figure 1). It is this separation in solution that makes them charged.
As you might suspect, when something is electrically charged, it can have either a positive or negative charge. This also is true of ions. In the case of sodium chloride dissolving, the sodium ion carries a positive charge, and the chloride ion carries a negative charge. Positively charged ions are called cations, and negatively charged ions are called anions.
Why Ion Exchange
Many ions can have negative effects - either on the mechanical parts of a process or in our bodies. For example, most people are aware of hardness deposits caused by calcium and magnesium or “blue baby” syndrome caused by nitrite in drinking water.No matter the source, these ions and more can be removed from water. In order to remove ions, however, it is necessary to know what is in the water. Just as ions can be either positively or negatively charged, ion exchange can be further subdivided into cation exchange or anion exchange.
A simple chemistry memory aid can help you figure out which is which. Positively charged cations generally end in “ium,” such as magnesium, sodium, calcium and radium. Negatively charged anions generally end in “ate,” “ite” or “ide,” such as sulfate, nitrite, chloride, etc. (see Figure 2).
Different ions also have different levels of positive or negative charge. Ions typically will form +1, +2, +3 or -1, -2, -3 ions, but can range higher in charge. Ions don't have to consist of just one element either. Many consist of several different atoms and are fairly complex.

The Importance of Resin
After all the discussion about ions in water and how they get there, the true discussion about ion exchange starts with resin. Resins are tiny plastic beads that act as the backbone, or structure, on which ion exchange can happen. Resins are made from different plastics and can be a variety of different colors (see Figure 3). They also can have a variety of different functions, which will be discussed in a moment.On a sub-microscopic level, it is useful to think of resin as a tiny ball of long strings all bunched together. Let's assume that in order to keep the ball from unraveling, some of the loops of string are tied together by shorter pieces of string, or ties, periodically throughout the longer strings.
In this example, the strings represent long polymer molecules of some plastic material, and the ties are a co-polymer, or tie molecule, that helps hold the material closer together. The beads also contain a lot of water that is bound into the string matrix. The water content of many resins ranges from approximately 40 percent to 50 percent.
Once manufactured, the resin beads can be chemically functionalized to serve a purpose. For example, resin destined to remove cations from water (such as calcium or magnesium hardness, or radium) would have to have opposing (negative) exchange sites introduced into the matrix of the resin bead. In other words, exchange sites could be placed at certain points on the strings.
Once these exchange sites exist on the polymer chains, they can be “loaded up” with positive ions that are more desirable than, for example, the unwanted calcium, magnesium or radium mentioned above. These ions then are exchanged into the water while the unwanted ions are retained at the exchange site(s). Hence the term “ion exchange.”
Many people incorrectly assume that ion exchange only happens on the surface of the tiny spherical beads. They also incorrectly assume that water flows through the beads. Ion exchange is more accurately described as the ability of ions to permeate, or diffuse, from the water outside a bead into the water bound inside the resin beads. Then exchange occurs, and the more desirable ions diffuse out of the bead into the surrounding water.
Applications
Now that the fundamental operation of ion exchange resin is understood, specific applications can be discussed. By far, the most widely known application of ion exchange is softening. As the name implies, softening simply is removal of the scale-forming hardness ions (calcium and magnesium) from water.Based on their names, it is easy to tell that the calcium and magnesium ions are positively charged cations. Thus, a cation resin is used.
After being in hardness-removal service for a period of time, the resin bed becomes loaded with water hardness cations, and it is time to “regenerate” the resin bed. Regeneration simply is a replenishing of the exchange ions. Most often, the exchanging cation used in softening is sodium, although potassium also is used.
Calcium and magnesium form (+2) ions in water, thus they tend to be more attracted to the exchange sites than the sodium (+1) or potassium (+1) ions held there during service. In the regeneration phase of operation, concentrated brine from a brine well is drawn slowly into the resin bed where it is able to overwhelm the calcium and magnesium (as well as other cations) held there. The hardness ions are displaced from the exchange site and sent to drain.
However, ion exchange is much more than softening. Negatively charged ions can be removed as well. Anions such as nitrate, sulfate, silicate, selenate, arsenate and many others can be removed using various anion resins.
One word of caution when dealing with health-based ion removals such as nitrate: Some ions have stronger attractions to exchange sites on resin than others. For example, the sulfate ion - which is very common in natural waters - is more strongly attracted to some anion resins than nitrate ion. If improperly selected for nitrate removal, some anion resins would preferentially remove sulfate instead of nitrate.
In other words, in the case of health-based contaminant removal, it is best to know which other competing ions are present in the water before selecting an appropriate resin. It also is best not to “cookbook” a treatment technique simply because it worked last time.
The Water Quality Association has several excellent sources on ion exchange and specific contaminant removal. The WQA has been testing and certifying the abilities of cation exchange water softeners to remove water hardness and to be safe and reliable for water treatment applications since 1960. Today, the WQA Gold Seal Program uses the NSFF/ANSI 44 Household and Commercial Cation Exchange Water Softeners standard for this purpose. The WQA Gold Seal Program currently lists more than 400 certified ion exchange water softener models.
Ion exchange is a highly versatile water treatment technology that tackles many different problems. Much of the information presented on ion exchange in this month's article will be covered in more detail during education and training at the WQA Aquatech USA 2005 show in Las Vegas from March 29-April 2, 2005.
Additional Resources
"Deionization Basics,” Water Quality Association, 1996, 39 pages.Practical Principles of Ion Exchange Water Treatment, D. L. Owens, 2nd Edition, Tall Oaks Publishing, 1995, 215 pages.
Ion Exchange Deionization for Industrial Users, W. E. Bornak, 1st Edition, Tall Oaks Publishing, 2003, 351 pages.
ND
Report Abusive Comment